|
 |
|
||||||||||
 |
 |
||
DOMAINATION Information |
DOMAINATION description
DOMAINATION infers structural domains in your query from alignments generated by from PSI-BLAST results. In addition, DOMAINATION improves finding distant homologies compared with PSI-BLAST. A complete description of the DOMAINATION method has been published and is available as PDF. The method, input and output are briefly described below.
DOMAINATION steps
DOMAINATION consists of two main parts: PSI-BLAST searches to find similar sequences and domain delinineation using the distribution of the sequences found over the query sequence. Details and parameters used are given below.
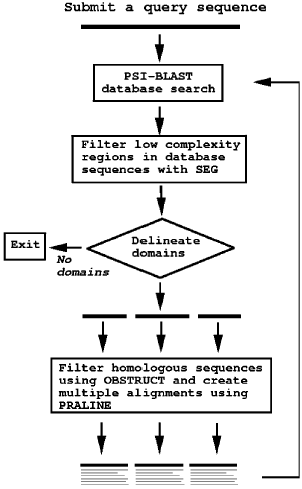
DOMAINATION starts with performing a database search (using the NCBI non-redundant protein database) of your query sequence with PSI-BLAST (with options -j4 -e0.001 -h0.0005). The resulting "hit" sequence fragments are filtered on low complexity (using SEG). Sequences with more than 15% low complexity regions are discarded. Next, domains are delineated using CHOP (as described in the article). CHOP assigns domain boundaries based on the distribution of the hit sequences over the query sequence. The minimum domain segment size is 10. CHOP produces a file with multiple FASTA sequences. These sequences are filtered to find the largest subset of sequences within a range of 20% to 60% sequence identity. OBSTRUCT is used for this filtering step. Thus, all sequences with less than 20% or more than 60% sequence identity are filtered out. The remaining sequences are aligned with Praline, a multiple sequence alignment program, to generate a "true" multiple sequence alignment instead of a master-slave alignment. This alignment is supplied for subsequent PSI-BLAST runs (also with options -j4 -e0.001 -h0.0005). In case PSI-BLAST finds a large number of hits for your query sequence, the DOMAINATION run can take over 15 minutes. Figure 1 summarizes the steps. The maximum number of iterations is set to 10. It is extremely unlikely to reach this number of iterations.Figure 1: Flow diagram of DOMAINATION.
DOMAINATION input
You can supply a protein sequence in FASTA format via the textfield or via file upload. Note that the only a single sequence should be supplied. You can choose to perform a sequence similarity search which will locally run NCBI's PSI-BLAST and FastA's SSEARCH (producing high quality Smith-Waterman alignments) on all sequences found by DOMAINATION. This will provide you with an overview of similarities between your query sequence and all sequences found during DOMAINATION's iterations.
DOMAINATION output
The output contains two parts: domain lay out and sequences found by DOMAINATION. In case PSI-BLAST did not find any hits, you will see an error message (PSI-BLAST did not find any hits for your query sequence!).
Domain lay out
Overall domain lay-out and domain lay-out per iteration is shown as a graphic. Mousing over a domain will display the domain boundaries (only on the output page). Clicking on a domain will highlight its sequence in the original query FASTA sequence. Clicking on the highlighted domain will extract its sequence. A graph with annotated domain boundaries is also available. Each domain of a query sequence will be send as query to further iterations. DOMAINATION works on FASTA sequences only. This means that you may find domains shorter than 10, since iterations are combined in our output. If a query is not split further into domains, this query will drop out of the iterations and become absent in tracks for higher iterations. For example, domain 3 in the graphic is not split in the second iteration. Therefore, it is absent in the third iteration.
Sequences found by DOMAINATION
This part reports the number of sequences found by all DOMAINATION iterations together. A file with all sequences found by DOMAINATION can be downloaded (in FASTA format). If you have choosen to perform the sequence similarity search, you will find links here to BLASTP and SSEARCH report, both in HTML and plain text formats. The report in HTML format contains a graphic which show the position of the top 100 hits on your query sequence. If you mouse over the hits the name, score and E-value of the hit will appear both in the text box at the top of the graph and as "pop up". These similarity searches are corrected for the size of the original non-redundant database. The command line options used are:
blastpgp -F T -z 1418577927: low-complexity filter is on and the size of the original database is used to calculate the E-values
ssearch35 -z 11 -s BL62 -B -Z 4113801: estimate the statistical parameters from shuffled copies of each library sequence (-z); use BLOSUM62 (-s); show normalized score as a z-score (-B) and use the number of sequences from the original database to calculate E-values.For more information, see the explanation on BLAST and FASTA.
Data download
The multiple sequence alignments generated by DOMAINATION can be opened in Jalview. To facilitate additional off-line analysis, generated data is available for download. This includes the domain sequences, multiple alignments, PSI-BLAST reports.
Example output
Complete example output is available here. The query protein was NP_543124.1, WD repeat domain 5 [Mus musculus].
(c) IBIVU 2025. If you are experiencing problems with the site, please contact the webmaster.